Evaluation results of red tourism resource efficiency in China
Evaluation of input–output efficiency of red tourism resources in China
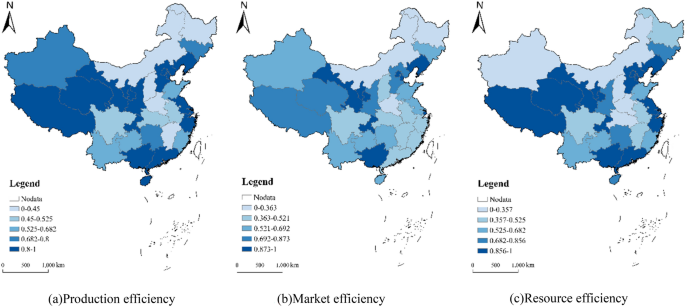
Equations (1) and (2) were used to evaluate the efficiency of 300 red tourism resources commissioned in China in 2022. These resources were categorized using the ArcGIS natural breakpoint method, yielding the mean efficiency values by province (Fig. 1).
Figure 1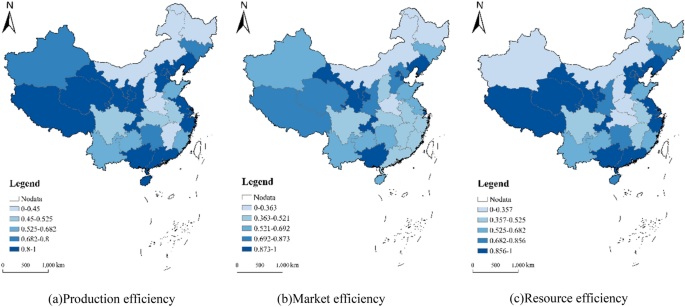
Spatial distribution of red tourism resource efficiency in China in 2022.
(1) China’s red tourism resources commissioning efficiency deviates from the frontier surface, showing the spatial characteristics of gradual decrease from east to west. In 2022, the average commissioning of China’s red tourism resources stood at 0.72. Notably, the commissioning, market, and resource endowment efficiencies vary significantly among different resource units and provinces, revealing an overall spatial trend of gradual decline from east to west. The evaluation results of resource units show that 12 of the 300 red tourism resource evaluation units are at the forefront of production (production efficiency is 1) (Fig. 1a). The market efficiency of 34 red tourism evaluation units is at the production frontier (Fig. 1b), and there are 25 red tourism resource endowment efficiency at the forefront (Fig. 1c).
(2) Decomposing the efficiency of China’s red tourism resources regarding input and output reveals the allocation capacity and technical innovation status of these resources. The mean pure technical efficiency of China’s red tourism resources is 0.611, demonstrating a spatial trend of Y. Evaluation results indicate that while the seven evaluation units at the production frontier maintain the highest pure technical efficiency, the unit with the lowest efficiency value changes, notably the former residence of Saifudin Aiz in Artux City, Kizilsu Kyrgyz Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Moreover, the pure technical efficiency of the 31 provinces demonstrates a spatial trend decreasing from east to west. The average pure technical efficiency of tourism resources in the east stands at 0.582, representing a 12.98% reduction from total production efficiency. Conversely, the pure technical efficiency of tourism resources in the West is the lowest at 0.254, reflecting the largest reduction (27.08%) compared to total production efficiency. Other regions similarly demonstrate smaller pure technical efficiencies, all exhibiting different degrees of decline relative to total production efficiency. These results underscore the low technical innovation capacity and the inadequate allocation of tourism resources as significant constraints on the improvement of production efficiency within China’s red tourism sector.
Results of the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources
The evaluation results of market input conversion efficiency show that the average value of market input conversion efficiency of China’s red tourism market in 2022 is 0.563, which is at a medium–low level, and the input conversion efficiencies of the number of travel agencies, the number of tourism employees and the number of hotels show a low-value equilibrium structure (Fig. 2a). The evaluation results of resource endowment input conversion efficiency show that the average conversion efficiency of China’s red tourism resource endowment input in 2022 is 0.573, which is at a low level, and the input conversion efficiency of factor value, environmental quality and resource development presents a low and unbalanced structure. However, the conversion efficiency of resource endowment input at the regional level presents a banded pattern of “flower arrangement” with high and low values (Fig. 2b).
Figure 2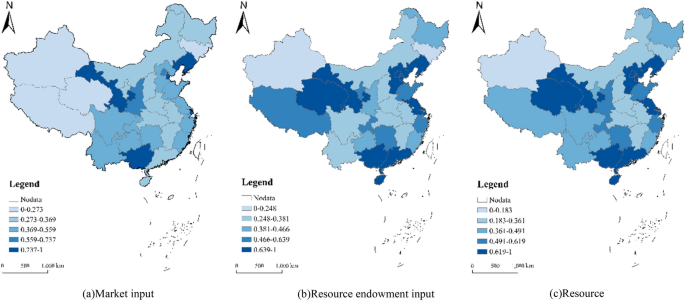
Spatial distribution of red tourism resource transformation efficiency in China in 2022.
China’s red tourism resources conversion efficiency lags behind the frontier, showing a “V-shaped” spatial pattern of local high values. 2022 China’s red tourism resources conversion efficiency average value is 0.549, the economic effect of the conversion efficiency (0.340) has become the main factor affecting the conversion efficiency of China’s red tourism resources. Regionally, the resource conversion efficiency as a whole shows a spatial difference of gradual change from east to west (Fig. 2c). The mean value of conversion efficiency is higher in the eastern provinces, and the high conversion efficiency of the social effect of tourism resources has become a factor driving the efficiency of conversion in the region; while the important factor limiting the region is the relatively low conversion efficiency of the economic effect, with the most prominent performance being in Beijing (1).
The developed transportation network in the east, coupled with the robust tourism consumption demand from rapid economic development, enhances conversion efficiency to varying degrees. The conversion efficiency of the western provinces is the highest at 1, and Qinghai Province is the highest area in China (1). The region’s red tourism resource conversion efficiency is characterized by high conversion efficiency of social effects and extremely low conversion efficiency. This structural pattern arises from the influence of the region’s rich geographic landscape tourism resources, which significantly improve the radiation and driving effect of red tourism, thereby improving social effect conversion efficiency. However, this influence does not extend to economic effect conversion efficiency, resulting in its pronounced disparity.
Under the influence of the “siphon effect” of the resources of architectural facilities and geographic landscape tourism, the flow preference of the market main body and the concentration of social concern have led to the lower conversion efficiency of economic benefits and public opinion effects. The conversion efficiency of the western region is 0.407 lower than that of the eastern and southern regions, but its composition of conversion efficiency is different, that is, the conversion efficiency of social effects is high but the conversion efficiency of public opinion effects is low. Owing to the imperfect red tourism market in the western region, imperfect transportation network conditions, and inadequate promotion of red tourism, the spillover effects of tourists’ “words and deeds” and tourism enterprises’ “advanced experience” in neighboring areas are insufficient, hindering the transformation of public opinion benefits.
Geographical exploration results of spatial differentiation of red tourism resources transformation efficiency in China
Impact factor test
To accurately identify the influencing factors affecting the spatial differentiation of China’s red tourism resources’ transformation efficiency, a logistic regression model was used to analyze the regression coefficients and multivariate covariance of the ten indicators (Table 2). The regression results indicate a significant positive correlation (p < 0.01) between the quality of human capital (E3), tourism market scale (E4), tourism industry scale (E5), urbanization level (E8), policy support strength (E9), and the spatial differentiation. Additionally, covariance diagnosis reveals a positive correlation among industry comparative interests (E1), product innovation ability (E2), transportation network conditions (E6), economic development level (E7), and scientific and technological information level (E10). However, factors (E7) and (E10) were excluded because of variance expansion coefficients exceeding 10. To validate the scientific validity of retained and excluded factors, the natural breakpoint method was used for classification, followed by spatial coupling and matching analysis with tourism resource transformation efficiency classes. The results revealed a high degree of overlap between factor types E3, E4, E5, E8, and E9 with class 0 (perfect match class), thus identifying these five factors as dominant factors affecting the spatial differentiation of red tourism resource transformation efficiency.
Table 2 The regression coefficients and multivariate covariance of the ten indicators.Influence detection results for dominant influence factors
To assess the influence of the influencing factors on the transformation efficiency of regional red tourism resources, geo-detectors were used to detect the 300 red tourism sites (transformation efficiency values) and their distribution areas (transformation efficiency mean values), and the following results were obtained: (1) The influence of the dominant influencing factors varied significantly, and the comprehensive influence of the external environment became the main source of influence. The dominant factors affecting the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources are E5, E8, E9, E3, and E4 in order at the 5% significance level, and their corresponding influences are 0.3565, 0.3237, 0.3132, 0.2458 and 0.1761, respectively. The combined influence of the external environment is 0.6369, and the combined influence of endogenous capacity is 0.7784, which is 0.1415 bigger than the influence of the external environment (Table 2).
The spatial differentiation of the influence of the dominant factors is obvious, showing a Y-shaped spatial pattern. In the provincial dimension, the combined influence of the red tourism resource transformation efficiency factor in Beijing, Tianjin, Gansu, Ningxia, Guangdong, and Hainan is at a high level. From the geographical partition dimension, the mean value of the integrated influence of the factors in the eastern region of China is 0.2653, forming a high-influence extreme zone, while the mean value of the low-influence extreme zone in the northwest is 0.0792. From the transformation efficiency partition dimension, the integrated influence of the factors in the synergistic zone of the tourism resources input and output efficiency is the largest at 0.4098, and the integrated influence in the zone of the transformation and upgrading of the efficiency of the tourism resources is the smallest at 0.2626.
Interaction detection results for dominant influence factors
(1) The interaction influence of two-factor is stronger than that of one-factor and dominated by nonlinearly enhanced interaction type. The factor interaction influences of the five types of regions of China’s red tourism resource transformation efficiency all show nonlinear enhancement and two-factor enhancement, and there is no independent and weakened relationship. Among them, E2, E9, E7, and E4 influence factor groups have high mean values of interaction influence compared to single-factor influence, and become the strongest factor groups influencing the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources. In the overall analysis, among the factor interaction types in the region, the nonlinear enhancement category is 51, accounting for 86.67% of the total number of groups, and the two-factor enhancement category accounts for 13.33% of the total number of groups. Analyzing the internal and external influence factors, the internal and external combined nonlinear increase interaction types accounted for 66.67% of the total number of groups, while the intra-group interactions were dominated by bifactor enhancement accounting for 53.33% of the total number of groups. The results show that the interaction of two factors have a more profound impact on the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources, and the cyclic cumulative effect of the combined influence of internal and external factors more realistically depicts the formation of its spatial differentiation pattern, and it becomes the key to the future enhancement of the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources and the high-quality development of red tourism.
(2) The two-factor interaction influence showed differences in internal and external types, and the cumulative cyclic effect of the endogenous ability factor group was more significant. Endogenous capacity factors become the dominant factors affecting the conversion efficiency of red tourism resources. The average interactive influence of influencing factors on the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources in 2022 is successively E2, E3, E4, E9, E6, and E7. Compared with the single factor influence, this result shows a big difference, that is, product innovation ability, human capital quality, tourism market scale, policy influence, and influence status increase. Among them, the factor with the biggest improvement is product innovation ability; The influence status of external environmental factors declined, and the most significant factor was traffic network conditions. Therefore, paying attention to the interaction and coupling of endogenous capacity influencing factors of red tourism resource conversion efficiency and promoting the integration and linkage of multiple policies without losing an opportunity provides a new direction for systematically improving the conversion efficiency. The interaction of internal and external factors is the main way of spatial differentiation of red tourism resource conversion efficiency. The most significant interaction effects of the external environment and endogenous capability factors are E2 ∩ E9, E3 ∩ E4, and E3 ∩ E7, whose average influence on the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources is as high as 0.5864, 0.5712, and 0.5608. The external environmental factors of transportation network conditions, economic development level, and policy support are the basis for the development of red tourism resources and the prerequisite for changes in transformation efficiency; The three endogenous factors of product innovation capability, human capital quality, and tourism market size serve as the core competitiveness of the development of red tourism resources and are the driving force for changes in transformation efficiency. Therefore, focusing on the linkage between internal and external factors provides a new way to improve the efficiency of transforming red tourism resources (Table 3).
Table 3 Influence of dominant factors of the transformation efficiency of red tourism resources in China in 2022.
(3) The difference of factor interaction influence in each sub-district is significant, which becomes the key to improving the transformation efficiency of red tourism resources. From the results of the interaction influence of each dominant factor on the transformation efficiency of China’s red tourism resources in the subregion, we get: that endogenous capacity and the external environment factor interaction are the most important ways to influence the transformation efficiency of tourism resources in different subregions, but presenting two-factor combination of the type of influence of the differentiation and the combination of the influence of the diversification of the mode of geographic characteristics (Table 4). The influence of the dominant factors are all high or low values of the regional internal and external interaction influence mode is simple but the combination type difference is significant. Among them, the six dominant factor influences in the synergistic zone of red tourism resources input and output efficiency are all high values and E2 and E9 (QE2 ∩ E9 is 0.1586) become the most significant types of interaction influences; the system supply leadership and scientific and technological innovation reliance become the advantages of promoting the transformation efficiency of red tourism resources represented by Beijing, and also the focus of the future polarization, which is the recommended paradigm for the high-quality development of red tourism. The influence of each dominant factor in the red tourism resources comprehensive capacity enhancement area is low, and E3 and E7 (QE3 ∩ E7 is 0.1498) become the types with the most significant interaction effects; the exploration of the linkage mechanism between tourism human resources cultivation and economic level is the focus of the concern for promoting the transformation efficiency of red tourism resources represented by Jiangxi. The regional interaction influence pattern and combination type of the influence differentiation of the dominant factors are complicated. Among them, the endogenous ability factor interaction of the red tourism industry comprehensive quality enhancement and efficiency area is significant, and the most prominent types of performance are E3 and E4 (QE3 ∩ E4 is 0.1279), which become the advantages of the region; while the shortcomings of the interaction influence of the external environment are E7 and E9 (QE7 ∩ E9 is 0.1005). Therefore, the complementary paths of appropriate evacuation of endogenous force energy, improvement of policy and institutional supply, and capital investment are the focuses of realizing the transformation efficiency upgrading of red tourism resources represented by Hunan. The external environment interactions in the red tourism resource efficiency transformation and upgrading area are dominated by E6 and E9 (QE6 ∩ E9 is 0.1213), but the interaction influence between E4, E3, and E7 is significantly smaller. Therefore, the implantation mode of enhancing endogenous capacity and the empowerment mode of the external environment becomes the key to promoting the growth of transformational efficiency of red tourism resources in the region. The internal and external interactions among E4, E6 and E9 in the comprehensive effectiveness cultivation area of red tourism resources are obviously in a weak position (QE4 ∩ E9, QE6 ∩ E9, QE4 ∩ E6 are 0.0981, 0.0936 and 0.0997, respectively), and the vitality of polarized market players, the enhancement of transportation accessibility and the policy guidance have become the key means to break the trap of the conversion efficiency of the red tourism resources in this region.
Table 4 Results of interactive detection on spatial differences of the transformation efficiency of red tourism resources in China in 2022.
Source link